HÖRST
Types of hearing loss
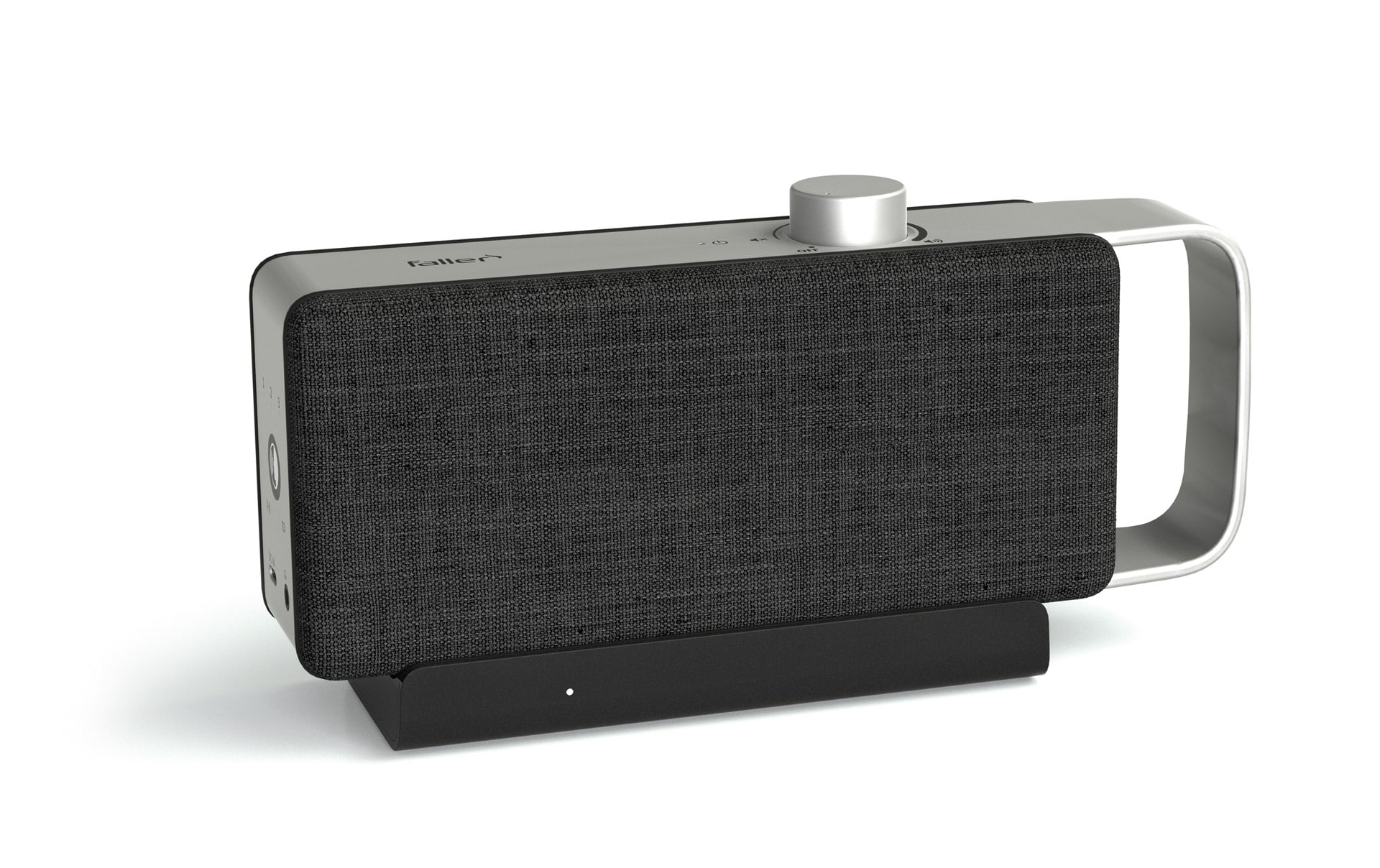


Table of contents
A detailed investigation
When we talk about hearing loss, many people only think of deafness. But did you know that there are many types of hearing loss, and that they can affect us all? Below, we take a closer look at the topic of "types of hearing loss."
What is hearing loss?
Simply put, hearing loss is a reduction in hearing that occurs either suddenly or gradually. It can have various causes and occur in many ways. You may suddenly find that you can no longer hear high-pitched sounds, or you may have difficulty holding conversations in noisy environments.
Hearing loss affects not only the volume but also the clarity of sounds and speech. In some cases, it can also lead totinnitus, a persistent ringing or buzzing in the ear. It is important to consult a specialist at the first signs to discuss possible treatment options.
The two main types of hearing loss
In general, hearing loss can be divided into two main types:
Conductive hearing lossaffects the outer ear or the middle ear. In this case, sound is not effectively conducted to the inner ear.
Conversely, sensorineuralhearing lossaffects the inner ear or the auditory nerve.
Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss is a specific type of hearing loss that occurs when the process of sound transmission from the outer ear through the ear canal to the middle ear—including the central structures of the eardrum and the three essential ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes)—to the inner ear is disrupted. This phenomenon prevents sound from reaching its destination efficiently and without significant loss, which can lead to hearing impairment.
The causes of this type of hearing loss are varied and can be of many different kinds. Some of the most common reasons include:
- Infections:These are primarily infections that lead to inflammation of the middle ear. This inflammation can impair the normal functions of the ear and lead to hearing problems.
- Blockages in the ear canal:Such blockages can be caused by foreign objects, excessive earwax, or even tumors. These physical obstacles can prevent the normal flow of sound, leading to conductive hearing loss.
- Eardrum problems:This can occur due to perforations, scarring, or other damage to the eardrum that impairs its ability to effectively transmit sound waves.
- Malformations of the ossicles:In some cases, an abnormal structure or malformation of the small ossicles, which are responsible for transmitting sound waves, can also lead to conductive hearing loss.
It is important to note that conductive hearing loss is not permanent in many cases and can be improved with appropriate medical or surgical treatment. These treatments aim to correct the underlying problems that prevent normal sound conduction, therebyimproving hearing.
conductive hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss, also known as sensorineural deafness, is a specific type of hearing loss in which the problem is located deep inside the ear. More specifically, the problem lies in the sensitive structures of the cochlea, also known as the inner ear, or in the auditory nerve. Both are central to the transmission of sound signals from the ear to the brain, where they are interpreted as acoustic information.
There are a number of typical causes that can lead to sensorineural hearing loss:
Unfortunately, the sad truth is that this type of hearing loss is often permanent. Unlike many other cells in the body, hair cells and the auditory nerve do not have the ability to regenerate or renew themselves. Therefore, the hearing loss caused by this damage is often irreversible. However, there are various treatment options available, including hearing aids and cochlear implants, which can help minimize the effects of this type of hearing loss and improve the quality of life for those affected.
- Age-related wear and tear of hair cells:With increasing age, the hair cells in the cochlea undergo natural wear and tear. Since these cells play an essential role in sound perception, their degeneration leads to a reduced ability to effectively capture and transmit sound.
- Noise pollution:Constant or intensenoise pollutioncan place considerable strain on hair cells and lead to their damage or complete failure. Workers in noisy industries are particularly at risk.
- Infections:Certain infections can affect the inner ear and cause damage to the hair cells or auditory nerve. These include some viruses and bacterial infections that can directly affect the inner ear.
- Ototoxic medications:Some medications are known to have harmful effects on hearing and can lead to sensorineural hearing loss. These include certain antibiotics, loop diuretics, and some cancer medications.
- Sudden hearing loss:In rare cases, sudden hearing loss can lead to sensorineural hearing loss. The exact causes of such sudden hearing loss are often unknown, but it is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
- Autoimmune hearing loss: Autoimmune diseases can affect various organ systems, including the sensitive hearing organ. In autoimmune hearing loss, the immune system mistakenly attacks structures in the inner ear. This can lead to progressive hearing loss. This rare but serious condition is often overlooked or confused with other forms of hearing loss. Early diagnosis and targeted therapy are crucial to prevent permanent damage to hearing.
Combined hearing loss
In some cases, people with hearing problems may have a particularly complex form of hearing loss known as mixed hearing loss. This form ofhearing lossis characterized by elements of both conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss. Strictly speaking, both the sound pathway through the ear and the ability of the inner ear to correctly interpret sound and send it to the brain are impaired.
This can lead to significant hearing loss and pose a particular challenge in treatment, as both aspects of the hearing process are affected. Nevertheless, there are various medical and technical approaches to dealing with this complex form of hearing loss and improving the quality of life of those affected.
How can you recognize hearing loss?
Hearing loss can sometimes be difficult to identify, especially in the early stages or when the degree of hearing loss is minor. In many cases, hearing loss is not obvious and can take subtle forms that make it difficult to recognize the presence of an impairment. Certain sounds, especially those with low volume or specific frequencies, may be difficult to hear or even inaudible.
Some of the first signs of hearing loss may include feeling that people around you are mumbling, having difficulty following conversations in noisy environments, or frequently asking for the TV or radio volume to be turned up. In addition, a tendency to withdraw from social interactions due to difficulty following conversations may also be an indication of possible hearing loss.
An audiogram, a type of hearing test, can help determine the degree and type of hearing loss. This test uses different frequencies and volumes of sounds to determine a person's specific hearing capacity.

Treatment options for hearing loss
The choice of appropriate treatment for hearing loss depends greatly on the specific type and degree of hearing loss a person experiences. Various therapeutic measures are available that aim to improve an individual's ability to perceive sound and thus enhance their quality of life.
One of the most common solutions for people with hearing loss, especially sensorineural hearing loss, is the use of hearing aids. Hearing aids are high-tech devices that pick up sound waves and amplify them so that they can be more easily perceived by the parts of the ear that are still functioning. They can be customized to a person's specific hearing needs, with different models available for different degrees and types of hearing loss.
In cases of profound hearing loss where hearing aids are not sufficiently effective, a cochlear implant may be a viable option. Cochlear implants are advanced medical devices that are surgically inserted into the ear and use electrical impulses to take over the function of damaged or non-functional parts of the inner ear. These impulses are then sent directly to the auditory nerve, bypassing the damaged areas and enabling the brain to receive sound information.
In some cases, there may be other treatment options. These include surgical procedures to treat certain types of conductive hearing loss, drug therapy to treat certain types of hearing loss caused by infection or inflammation, and audiological rehabilitation, which offers techniques and strategies to improve hearing skills and communication abilities.
Support in everyday life: TV hearing amplifier
Another innovative solution for improving hearing quality in everyday life are TV hearing amplifiers such as the OSKAR from faller audio. Thanks to special dialogue optimization, the OSKAR enables users to better understand dialogues and speeches on the television—a perfect complement to a hearing aid. This makes watching television a relaxed and enjoyable experience again, even for people with hearing loss.
Further articles

Healthy candy alternatives for seniors

Cooking together in old age
